Troubleshooting¶
If you’re running into issues with your AtoM installation, there are several maintenance actions and command-line tasks you might want to try using to see if they resolve the issue, prior to seeking external support. This page will outline some of the most common issues, and how to resolve them.
Tip
If you are new to working with the Unix command-line, you might find the following slide deck useful to get started:
Jump to:
- Figure out the nature of the problem
- Error logs and Debug mode
- Restarting services
- Monitoring active processes and checking execution limits
- Running AtoM’s most common maintenance tasks
- Dealing with data corruption
- Getting support
- Troubleshooting FAQ
See also
Figure out the nature of the problem¶
The first thing you should do is try to isolate exactly what is causing the issue. Specifically:
- What are the exact steps required to reproduce this issue?
- What is the error encountered?
- What is the expected outcome?
Being able to articulate these clearly will often help you figure out what solutions you should try first - and if you can’t resolve the issue, you’ll need this information to seek further support.
It’s also useful to try to rule out any factors that are unrelated to the issue. For example: can you reproduce the error using a different browser? What about a different computer? If your AtoM site is publicly accessible, does it behave differently if accessed from home as opposed to work (i.e. might firewalls, VPNs, or other restrictions be affecting your access)? Is the issue particular to a specific user or group, or does it affect all users? If it’s an error related to a task supported by the job scheduler, is it just this one task that isn’t working, or are all jobs failling? And so forth.
With a detailed step-by-step guide to reproducing the issue, we can now better diagnose the problem and consider what we can try to resolve it.
Error logs and Debug mode¶
It can be useful to see if there is further information available on the nature of the error in your webserver logs, particularly if you have encountered a 500 internal server error:
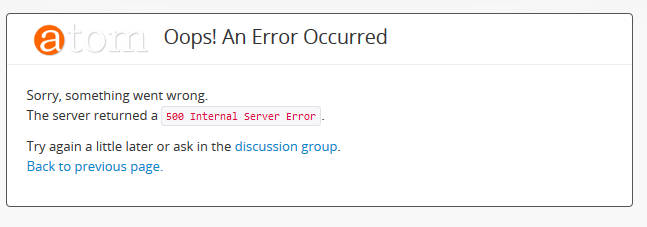
For information on accessing the webserver logs, see:
Another thing you can try to collect more information on the nature of the error is to see if a stack trace is available. This is particularly useful if the error results in a blank screen.
To check, you can try putting the application into Debug mode. More information on how to use Debug mode can be found here:
Tip
We also have a command-line tutorial video that will walk you through how to enable Debug mode and check your Nginx error logs, available here:
Note: The commands used in this video for restarting PHP-FPM is for Ubuntu 14.04 with PHP 5.x, which is no longer supported after version 2.4. For more recent instructions on restarting PHP-FPM, see below:
Restarting services¶
AtoM makes use of several PHP extensions, services, and libraries that are used to support the functionality of the application. These are not managed directly by AtoM or Symfony, and their use and location will depend on your particular installation environment. The following commands assume you have followed our recommended installation instructions - if you have made changes, some of the commands may be different in your installation.
Restarting services can be a useful first step in trying to resolve issues - if the service is in a bad state as a result of an error that has occurred, then restarting it can often return it to a working condition. Below are basic instructions for restarting PHP-FPM, Memcached, Nginx, and the atom-worker.
Jump to:
Restarting PHP-FPM¶
What
PHP-FPM is a PHP extension that allows for better interaction with an application’s web server, via the use and configuration of FastCGI pools in PHP. In AtoM’s default installation configuration, Nginx will proxy PHP requests to PHP-FPM.
FastCGI is a binary protocol for interfacing interactive programs with a web server. FastCGI is a variation on the earlier Common Gateway Interface (CGI); FastCGI’s main aim is to reduce the overhead associated with interfacing the web server and CGI programs, allowing a server to handle more web page requests at once.
When
You should consider restarting PHP-FPM if:
- You have made any changes to your web server configuration
- You have made any changes to AtoM’s configuration files
- You have made any changes to the PHP pool set up during installation
- You are trying to ensure all application caches are cleared
How
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
See also
Restarting Nginx¶
What
Nginx (pronounced “engine x”) is an open source HTTP web server (among other things). It manages the interaction between your web browser and AtoM. Your browser requests a page in AtoM, and this is sent to Nginx, which communicates with AtoM to retrieve and serve the page, or else returns an error message.
When
You should consider restarting Nginx if:
- You’ve made changes to your web server configuration
How
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Restarting memcached¶
What
Memcached is an open-source, general purpose distributed memory object caching system. It is often used to speed up dynamic database-driven websites by caching data and objects in memory to reduce the number of times an external data source (such as a database) must be read.
See also
when
You should consider restarting Memcached if you’re using it when:
- You are trying to ensure all application caches are cleared
How
sudo systemctl restart memcached
See also
Restarting the Job scheduler¶
What
AtoM relies on a job scheduler in order to execute certain long-running tasks asynchronously in the background (instead of synchronously via your web browser, making you wait until the task is done and the page loaded before continuing), to guarantee that web requests are handled promptly and work loads can be distributed across multiple machines. Example tasks in AtoM that use the job scheduler include:
- Generating finding aids
- Importing records via the user interface
- Exporting records via the Clipboard
- Using the Move module to reorganize archival description hierarchies
- Ingesting DIPs from Archivematica
We use Gearman as our job scheduler in AtoM. Gearman “provides a generic application framework to farm out work to other machines or processes that are better suited to do the work. It allows you to do work in parallel, to load balance processing, and to call functions between languages.”
See also
When
You should consider restarting the atom-worker if:
- You have encountered a 500 error related to a task in AtoM supported by the job scheduler
- You have made changes to the worker configuration
- You have a job that never seems to complete in the queue
How
sudo systemctl restart atom-worker
Tip
If the worker hits the start rate limit (3 starts in 24h) to be able to start it again after fixing the issue, the failed status has to be cleared:
sudo systemctl reset-failed atom-worker
sudo systemctl start atom-worker
Also, if you have multiple jobs that never seem to complete stuck in the queue, you may also want to kill the queue itself, and then restart the atom-worker. The following task will clear all jobs from the queue (including those currently running, so be careful), as well as clear the job history of previous jobs from the database. This means you will need to manually restart any jobs you would like to continue via the AtoM user interface after running this command:
php symfony jobs:clear
Tip
A system administrator can also use SQL to kill just a specific stalled job, if you don’t want to lose other jobs in the queue, and/or the job history. For more information, see:
Other useful commands for managing the AtoM worker:
sudo systemctl enable atom-worker # Enables the worker (on boot)
sudo systemctl start atom-worker # Starts the worker
sudo systemctl stop atom-worker # Stops the worker
sudo systemctl status atom-worker # Obtains current status
For more detailed information on managing the job scheduler and the
atom-worker, see:
Monitoring active processes and checking execution limits¶
In some cases, your errors may be caused by a lack of resources - CPU, disk space, and/or memory - or because you’ve encountered the limits imposed by your PHP configuration. If this is the case, you might need to make changes to the PHP pool configuration or allocate more resources to your server.
Monitoring active processes with htop¶
Before we make any changes, it can be useful to do some basic monitoring - is this a temporary spike, or an ongoing issue? Can you reproduce the issue while monitoring resource usage and see any correlation?
If you’re familiar with the top command in Linux, this can be a useful way
to quickly view all active processes. However, we find htop to be a slightly
more user-friendly version of this. You can use Ubuntu’s package manager to
install it:
sudo apt-get install htop
To launch htop in your terminal simply enter htop. The console will display
a text-mode graph of your CPU, memory, and swap usage at the top of the page,
with a detailed list of processes provided below. This should give you a better
sense of whether or not you have enough resources allocated to your AtoM server.
It can also be useful to try to reproduce the error(s) you are encountering
while monitoring.
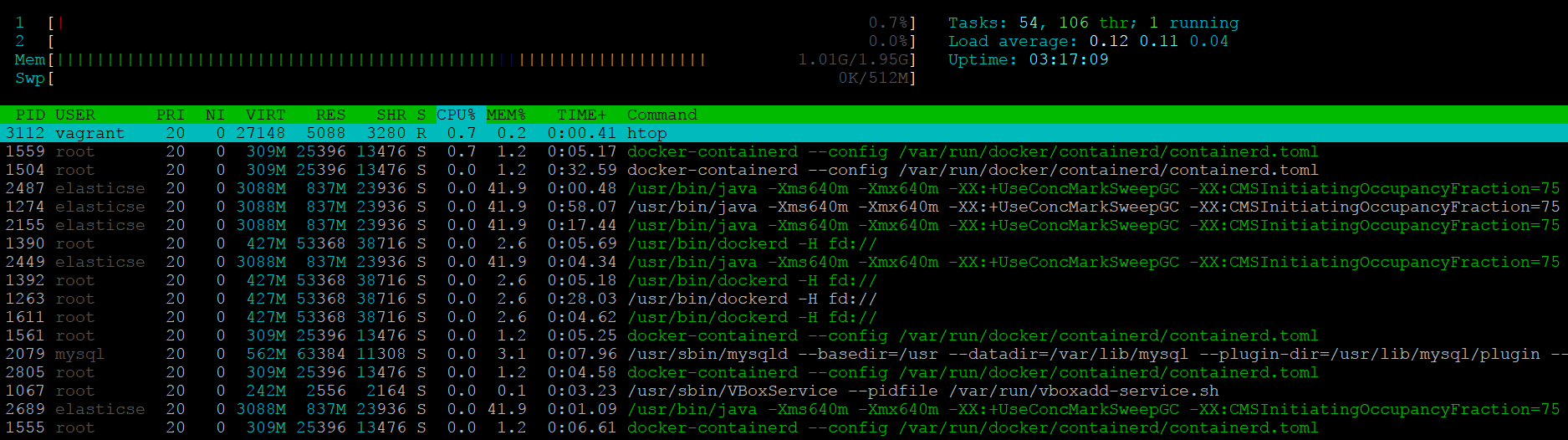
See also
More information on using top:
- http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/focal/man1/top.1.html
- https://www.lifewire.com/linux-top-command-2201163
More information on using htop:
Adjusting PHP execution limits¶
PHP includes several execution limits which are either configured during AtoM’s installation, or are set as defaults when PHP is installed. If you’ve encountered an error, and the web server error log includes a message like:
Fatal error: Maximum execution time of 60 seconds exceeded in ...
or:
Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 67108864 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 233734 bytes) in ...
…then you might want to consider changing PHP’s execution limits. For more information, see:
Important
Some PHP settings are configured in the PHP pool set up during installation, and should be adjusted there. See for example:
Remember, if you make any changes to your PHP settings (either in the php.ini
file, or in your application PHP pool), you will need to restart PHP-FPM after
saving your changes. See:
Running AtoM’s most common maintenance tasks¶
A great deal of issues in AtoM can be resolved by running some of the most common command-line and maintenance tasks included in the application. Some brief details on each, and when you might want to use them, are included below.
See also
There are many other useful command-line tasks in AtoM that can also be useful during troubleshooting. For detailed information on each task, see:
Prefer to see this information in a slide deck? Check out:
Jump to:
- Get information about your search index
- Populating the search index
- Clearing the application cache
- Rebuilding the nested set
- Generating slugs
Get information about your search index¶
What
AtoM maintains an Elasticsearch search index to provide fast, full-text search results with faceting. It is this index that allows AtoM to find and display records in the user interface when browsing and searching. During the installation process, we need to configure the host, port, and index name to be used in AtoM. Once records have been added to AtoM, they are indexed by Elasticsearch to aid in discovery via the user interface.
This task will allow a system administrator to review the status of AtoM’s Elasticsearch index without having to access any configuration files. The task output will include:
- Elasticsearch version
- Search host
- Port
- Index name
- Document index status for all primary entity types in AtoM (including Accession, Actor, AIP, Function, Information object, Repository, and Term)
When
You might consider running this task if:
- Records seem to be missing from the user interface
- No records are showing in search or browse at all
- You are having trouble connecting to the search index
- You are seeking support and you suspect the issue might be search index related
Basic usage
php symfony search:status
For more information, see: Check the status of your Elasticsearch index
Populating the search index¶
What
AtoM maintains an Elasticsearch search index to provide fast, full-text search results with faceting. It is this index that allows AtoM to find and display records in the user interface when browsing and searching.
Running this task will delete the current index, then repopulate and optimize the index. Depending on the number of records in your installation, this can take a while to run - for production sites, we recommend running this task after regular business hours.
Tip
If you don’t need to reindex all entity types, you
might want to try using the task’s --exclude-types option. See the full
task documentation for more details:
When
You might consider re-populating the search index if:
- Records seem to be missing from the user interface
- No records are showing in search or browse at all
- You have recently imported records from the command-line
- You have added a new language via the user interface Admin settings
- You have tried to perform an operation via the user interface that lead to a timeout
Basic usage
php symfony search:populate
For more information and additional options, see:
Tip
Do you keep getting warnings in the console when running the search:populate
command? If so, you may have to resolve some data corruption issues first.
See below, Dealing with data corruption.
Clearing the application cache¶
What
The Symfony 1.x framework that AtoM is built upon includes the ability to cache HTML content, for better responsiveness to HTTP requests.
One of the ways to speed up an application is to store chunks of generated HTML code, or even full pages, for future requests. This technique is known as caching, and it can be managed on the server side and on the client side.
…The principle of HTML caching is simple: Part or all of the HTML code that is sent to a user upon a request can be reused for a similar request. This HTML code is stored in a special place (the cache/ folder in symfony), where the front controller will look for it before executing an action. If a cached version is found, it is sent without executing the action, thus greatly speeding up the process. If no cached version is found, the action is executed, and its result (the view) is stored in the cache folder for future requests.”
From the Symfony docs
Occasionally, when errors occur or changes have been made, we need to flush
the cached HTML so we are being served updated content, and not an outdated
version of a web page. Running the cache:clear command will empty out the
existing application cache so it will become repopulated overtime with updated
versions of the web pages in AtoM as they are served to you.
When
You might want to try clearing the application cache if:
- You have made changes to AtoM’s configuration files
- You have recently encountered an error, and are testing to see if it’s resolved
- You are seeing something outdated or unexpected in the user interface
- You want to ensure you are seeing the current version of a page
- You have gotten a blank screen error that mysteriously works fine when the application is in Debug mode
Note
Because AtoM is session based, clearing the web browser cache might log you out of the application. Be sure you have saved any work you are doing in the user interface saved before doing so.
Basic usage
php symfony cc
For more information, see: Clear cache
Important
There are also other caches to consider clearing!
PHP-FPM (a PHP extension that AtoM uses) can also cache some content - if you are clearing the application cache, you should also consider restarting PHP-FPM. See above:
Memcached is also an external cache engine that can be used with AtoM - you should restart it as well. See above:
Finally, don’t forget that your web browser has its own cache - in some cases, if you are not seeing changes take affect, you might want to try clearing your web browser cache. Note that, because AtoM is session based, clearing the web browser cache might log you out of the application. Be sure you have saved any work you are doing in the user interface before doing so.
Rebuilding the nested set¶
What
AtoM generally uses a relational database to store its data (generally, MySQL). However, relational databases, which are comprised of flat tables, are not particularly suited to handling hierarchical data.
As developer Mike Hillyer notes, “Hierarchical data has a parent-child relationship that is not naturally represented in a relational database table.” One method of addressing this is to employ a “Nested set model” (Wikipedia).
AtoM makes use of a nested set to manage hierarchical relationships, such as between parent and child terms and descriptions. Sometimes, during operations that involve updates to large hierarchies, the nested set can become corrupted - especially if the server times out during an operation that reaches the execution limit settings. This task will rebuild all nested sets in AtoM.
When
You might consider rebuilding the nested set if:
- You are seeing strange behavior and/or missing records in the treeview
- You have attempted a long-running task that has timed out, causing it to fail midway
- You have gotten a 500 error, and the web server logs include something like:
Parent Resource id: 'XXXXX' does not exist
Basic usage
php symfony propel:build-nested-set
For more information, see: Rebuild the nested set
Important
You should also run the search:populate task to re-index your site
after rebuilding the nested set. For more information and task options, see:
Generating slugs¶
What
A slug is a word or sequence of words which make up the last part of a URL in
AtoM. It is the part of the URL that uniquely identifies the resource and
often is indicative of the name or title of the page (e.g.: in
www.yourwebpage.com/about, the slug is about). The slug is meant to
provide a unique, human-readable, permanent link to a resource. You can read
more about slugs in AtoM here: Notes on slugs in AtoM.
In some cases, AtoM may time out in the middle of an operation that involves the creation of new records. In such cases, it is possible that AtoM has died after creating an information object, but before having a chance to create a slug for the record. This can cause unexpected errors in the application - most notably, 500 errors when trying to access the records missing slugs through the application interface. This task will generate new slugs for any that are missing them in the database.
When
You might want to try re-generating slugs if:
- You have timed out while attempting an operation that creates new records, such as an import, or saving a large description
- You have gotten an error or warning while trying to populate the search index with a message that includes something like: “Couldn’t find information object (id: XXXXX)”
- You suspect the error you’ve encountered may be due to data corruption
- You have made changes to the description permalink settings and want to update existing slugs to match these settings
Basic usage
php symfony propel:generate-slugs
For more information, see: Generate slugs
Important
You should also run the search:populate task to re-index your site
after generating slugs. For more information and task options, see:
Dealing with data corruption¶
Data corruption refers to errors in computer data that occur during writing, reading, storage, transmission, or processing, which introduce unintended changes to the original data. In AtoM, this often means missing or incorrect values written to the MySQL database when a transaction fails to complete. Depending on the nature of the corruption, this can sometimes exist in your data for a long time before causing any noticeable issues.
Data corruption can happen in AtoM when large operations are aborted mid-process - for example, attempting a large move, publication status update, or import via the web-based user interface, and having it time out before the task completes. As of AtoM 2.3, database transaction support in MySQL was added to AtoM, which should reduce the likelihood of corruption - if an operation times out, then the database should automatically roll back to the last known good state. However, if you continue to experience errors in AtoM and have attempted many of the steps above without result, then it’s possible that you’ve encountered some corrupt data, and will need to perform some manual checks and fixes to address it.
Data corruption can occur in any entity type in AtoM, but it seems to occur most frequently among information object data - AKA archival descriptions, likely due to the fact that there tends to be many more descriptions than other entity types in a typical AtoM installation, and information objects are one of the few entity types in AtoM organized hierarchically.
It is beyond the scope of this documentation to cover all possible forms of data corruption. Instead, the sections below will provide solutions for the most common forms of information object data corruption, followed by further resources should you need to inspect and fix data corruption in other entity types.
Data corruption in information objects¶
The most common forms of database corruption among information objects (AKA archival descriptions) in AtoM tend to be due to one of the following:
- Missing slug
- Missing publication status ID value
- Missing object row values
You can use SQL to check the status of your information objects and see if all necessary values are present.
Tip
For basic information on accessing the MySQL database in AtoM from the command-line, see: the following section in the Common AtoM database queries page:
The following SQL query will output a 4-column table of information objects - the columns include the information object ID, the object ID, the publication status ID, and the slug for all descriptions. If any of the resulting rows are missing values, this will cause the search population task to throw warnings, and may cause other unexpected errors.
SELECT io.id as io_id, obj.id as obj_id, st.status_id as pub_status_id, slug.slug
FROM information_object io
LEFT JOIN object obj ON io.id=obj.id
LEFT JOIN status st ON io.id=st.object_id AND st.type_id=158
LEFT JOIN slug ON slug.object_id=io.id;
The resulting output should look something like this:
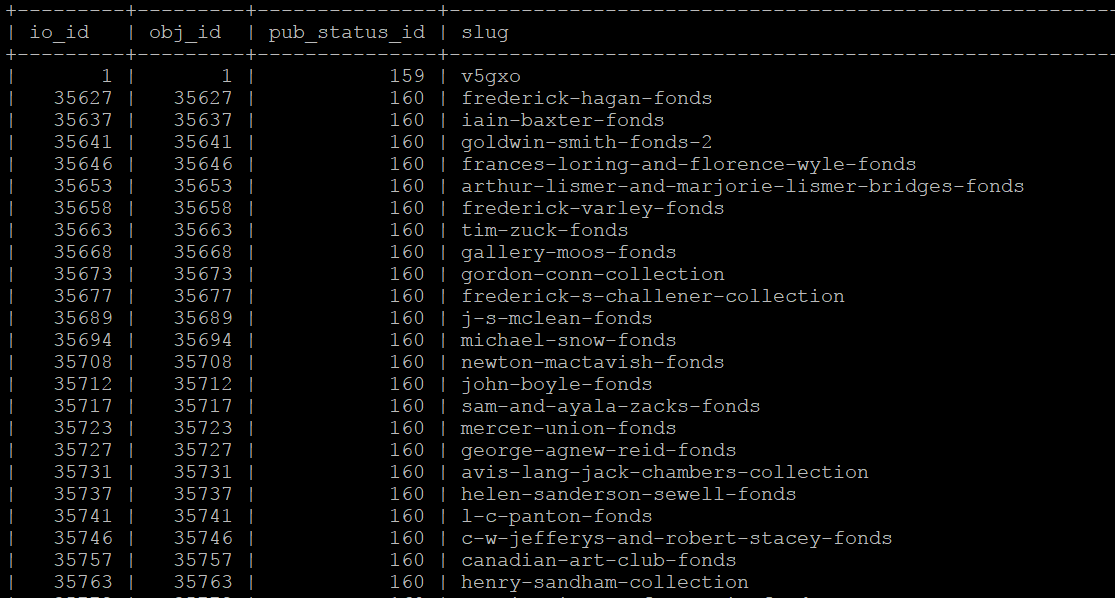
If you see rows with missing slugs, you can use the slug generation task to resolve this. See above - Generating slugs.
If you see rows with missing publication status ID values, then you can
use SQL to replace these values for each missing instance. You will need to
know the information object ID for the target row (listed in the first column
of the table shown above). In the following example query, XXXXX
represents where the object ID should be added. The third value, represented
by YYY in the example below, will be the publication status ID value - use
159 to mark the target record as Draft, and 160 to mark the target record as
Published.
INSERT INTO status (object_id, type_id, status_id, id, serial_number)
VALUES ('XXXXX', '158', 'YYY', NULL, '0');
For example, if you found a row with an information object ID value of 35777
that was missing a publication status, and you wanted to mark it as Draft:
INSERT INTO status (object_id, type_id, status_id, id, serial_number)
VALUES ('35777', '158', '159', NULL, '0');
If you see rows with a missing object ID then congratulations, you have encountered a rarer form of data corruption! You have two options for addressing this issue.
The first option is to simply delete the entire row in AtoM - this should cascade across other related tables. This solution will only work if the target row is not a parent record of other descriptions.
Warning
This means you are completely deleting this description from AtoM, and will need to recreate it manually via import or via the user interface at a later date.
To delete the affected row, you will need to know the information object ID
for the target row (listed in the first column of the table shown above). In
the following example query, XXXXX represents where the object ID should
be added:
DELETE FROM information_object WHERE id=XXXXX;
For example, if you wanted to delete an information object with an io_id
value of 39447, enter:
DELETE FROM information_object WHERE id=39447;
We recommend that after deleting the affected row via SQL you rebuild the nested set to resolve any corruption in the hierarchy resulting from your changes.
The second option is to manually insert an object row for the affected record.
To do so, you will need to give it a creation date and time, a last-modified date
and time, and you’ll need to know the information object ID of the target record.
The created_at and updated_at values can be made up or approximated, and
they can also be the same if that’s easier. In the following example query,
replace YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss with your chosen created_at and updated_at
values, and replace XXXXX with the information object ID of the target record:
INSERT INTO object (class_name, created_at, updated_at, id, serial_number)
VALUES ('QubitInformationObject', 'YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss', 'YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss', 'XXXXX', '0');
For example, if you wanted to say your information object was created on January 1st,
2016 at 1pm, last updated on February 25th, 2018 at 11:45am, and it has an
information object ID of 63172, then you could construct the SQL query like so:
INSERT INTO object (class_name, created_at, updated_at, id, serial_number)
VALUES ('QubitInformationObject', '2016-01-01 13:00:00', '2018-02-25 11:45:00', '63172', '0');
Again, we recommend that after making these changes you rebuild the nested set to resolve any corruption in the hierarchy resulting from your changes.
Finally, there is one other data corruption edge case which can happen in rare circumstances: when an information object ends up with a duplicated publication status.
You can check for descriptions with a duplicated publication status in your database with the following query:
SELECT
st.object_id, st.type_id, st.status_id
FROM status st
INNER JOIN (SELECT
object_id, type_id, COUNT(*) AS count
FROM status
WHERE type_id=158
GROUP BY object_id, type_id
HAVING COUNT(*)>1
) dt ON st.object_id=dt.object_id and st.type_id=dt.type_id;
The following query can then be used to remove one of the duplicated publication
statuses from the affected records. In the following example, we will remove the
draft status with the publication status ID value of
159 in the last part of the query - to remove duplicated
published statuses, change this value to 160:
DELETE st1
FROM status as st1, status as st2
WHERE
st1.object_id = st2.object_id
AND st1.type_id = st2.type_id
AND st1.id > st2.id
AND st1.type_id = 158
AND st1.status_id = 159;
As with the other examples above, we recommend that after making these changes you rebuild the nested set to resolve any corruption in the hierarchy resulting from your changes.
Data corruption in other entities¶
As noted above, data corruption can potentially occur in any entity type in AtoM, but it is beyond the scope of this documentation to provide a solution to every possible issue. If you think you are encountering data corruption in another entity type in AtoM, you’ll need to do some research! We have collected some resources below to assist you.
First, we make copies of the AtoM database’s Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) available on the AtoM wiki. An ERD is a data modeling technique that graphically illustrates an information system’s entities and the relationships between those entities. The AtoM ERDs can help you understand what tables exist in the AtoM database and how they are related. You can find them on our wiki here:
We also have some slides that will introduce you to using SQL queries in AtoM, available here:
There are also several utilities that can be used to provide a graphical user interface when exploring AtoM’s MySQL database. Two popular utilities that have been successfully used with AtoM include:
- MySQL Workbench: https://www.mysql.com/products/workbench/
- PHPMyAdmin: https://www.phpmyadmin.net/
Finally, be sure to double-check the MySQL reference documentation for your version for further tips on constructing SQL queries.
Below are a few extra SQL queries that might be useful when troubleshooting data corruption in other entity types.
Repository records
Finding a repository object ID when you know the slug:
SELECT object_id FROM slug WHERE slug='your-institution-slug';
Terms
Return the ID of all terms in a particular taxonomy (replace Taxonomy name
in the example below with the name of the target taxonomy):
SELECT term.id, term_i18n.name
FROM term
LEFT JOIN term_i18n ON (term.id = term_i18n.id)
WHERE term.taxonomy_id = (SELECT id FROM taxonomy_i18n WHERE culture = 'en'
AND name = 'Taxonomy name') AND term_i18n.culture = 'en';
Return the number of times a term is linked to a description, sorting terms from
most used to least. This will return all terms across taxonomies - if youw want
to see only one particular term, uncomment (aka remove the # at the start of
the line) the WHERE line and add the target term ID in place of the XXX:
SELECT DISTINCT term_id, term_i18n.name, count(term_id) AS CountOf
FROM object_term_relation
JOIN term_i18n ON term_i18n.id = term_id and term_i18n.culture = 'en'
#WHERE term_id = XXX
GROUP BY term_id
ORDER BY CountOf desc;
See also
Getting support¶
If none of the above suggestions have resolved your issues, it may be time to seek outside assistance. Remember, before seeking support, you should be able to clearly articulate the issue you are encountering, and provide detailed information on your installation environment. See above, Figure out the nature of the problem for suggestions.
The AtoM User Forum is a great way to seek input from other AtoM users and Artefactual, the lead developers of the application. We have a wiki page with more information on the user forum, here:
Before posting, we strongly encourage you to read the above page, especially the code of conduct and What should I include in a post sections.
We also encourage you to search the forum and browse related threads for suggestions before posting.
Tip
Did you know that posts in the AtoM User forum are now tagged by topic, and tags can be browsed to find related previous threads? For more information on how to use the tags in the forum (including how to tag your own posts), and a full list of available tags, see:
If you have reviewed our documentation, tried the suggestions in this troubleshooting page, and searched the forum for related issues and are still encountering errors, you can start a new thread in the user forum.
Be sure to include the following information in any support-related post:
- Your full AtoM version number - see: Application version
- Details on your installation environment, such as:
- Did you follow our recommended installation instructions?
- If no, what have you changed? Tell us more about your environment
- Any stack trace or web server error logs relevant to the issue - see: Error logs and Debug mode
- Detailed steps to reproduce the issue - see: Figure out the nature of the problem
- Information on any steps you have already tried to resolve the issues
- If you think the issue might be related to the search index, it can be helpful
to include the basic output of the
search:statustask in your post - see: Check the status of your Elasticsearch index - Anything else you think will be useful - including screenshots if that will help other users better understand the issue
Including a useful and descriptive title for your thread will also help other users reference the thread in the future if they encounter similar issue.
Troubleshooting FAQ¶
Below are some initial troubleshooting suggestions for frequently asked questions.
Jump to:
- Why do I get a blank white screen?
- Why do I get a 500 (Internal Server) error?
- Why do I get a “Max execution time” exceeded error?
- Why do I get a “Allowed memory size” exhausted error?
- Why do I get a “Too many connections” error?
- Why do I get a “MySQL has gone away” error?
- Why do I get a “Parent Resource id: ‘XXXXX’ does not exist” error?
- Why do I get warnings when populating the search index?
- Why do I get a SearchPhaseExecutionException when trying to search?
- Why do I get a 504 Connection timed out error?
- Why am I seeing strange behavior in the AtoM treeview?
- Why can’t I upload (large) digital objects?
- Why can’t I log into AtoM?
- What should I do if I get an error that isn’t described here?
Why do I get a blank white screen?¶
A blank, white screen in AtoM means that an error has occurred when loading the page. AtoM usually supresses error messages in production mode for security reasons, so the first thing to do is put the application in Debug mode, then re-try whatever you were doing when you got the white screen. See:
If the page loads with no errors in Debug mode, then you probably just need to clear the application cache to fix the regular (not in debug mode) webpage. See:
If you get an error message, please see if it is addressed below.
If you still get a blank, white screen you will have to check your web server error log for error messages. See:
Why do I get a 500 (Internal Server) error?¶
The 500 error is a very general HTTP status code that indicates a problem in the web server. You will need to check your web server error logs first, to get more information about the nature of the error. See:
One common cause of 500 errors in AtoM is when AtoM attempts to run an asynchronous, but the job scheduler is not running as expected. You will know this is the case if you see the following message in the webserver error log:
"No Gearman worker available that can handle the job."
If this is the case, we recommend restarting the atom-worker and then
re-trying the task that led to the 500 error. For more information on managing
the atom-worker and the job scheduler, see:
If you’re not sure what to do with the error message you find, and it is not addressed in the other FAQ sections below, then you can collect as much information as you can, search the AtoM User Forum, and start a new thread if you are unable to find anything relevant that will help you resolve the issue. See:
Why do I get a “Max execution time” exceeded error?¶
If you get an error like the following:
Fatal error: Maximum execution time of 60 seconds exceeded in ...
Then you may need to increase your PHP max_execution_time settings. See
PHP script execution limits for instructions on how to change PHP settings:
Why do I get a “Allowed memory size” exhausted error?¶
If you get an error like the following:
Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 67108864 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 233734 bytes) in ...
Then you may need to increase your PHP memory_limit settings. See
PHP script execution limits for instructions on how to change PHP settings:
Why do I get a “Too many connections” error?¶
If you get an error like the following:
500 | Internal Server Error | PropelException
Unable to open PDO connection [wrapped: SQLSTATE[08004] [1040] Too many connections]
This is a problem in MySQL, please refer to its documentation - make sure you are looking at the correct documentation for the version of MySQL have have installed. Below is a relevant link for MySQL 8.0:
See also
Why do I get a “MySQL has gone away” error?¶
If you get an error like the following:
500 | Internal Server Error | PropelException
[wrapped: SQLSTATE[HY000]: General error: MySQL server has gone away
This is a problem in MySQL, please refer to its documentation - make sure you are looking at the correct documentation for the version of MySQL have have installed. Below is a relevant link for MySQL 8.0:
It may be helpful to increase the level of verbosity in the MySQL logs to see if more detailss are available. From the MySQL documentation:
You can get more information about the lost connections by starting mysqld with the
--log-warnings=2option. This logs some of the disconnected errors in thehostname.errfile. See Section 5.4.2, “The Error Log”:
See also
Why do I get a “Parent Resource id: ‘XXXXX’ does not exist” error?¶
Usually this error is due to corruption of the nested set hierarchy of the resource (e.g. archival description, taxonomy term). This can usually be corrected by running the CLI task to rebuild the nested set:
php symfony propel:build-nested-set
For more details on this command, see:
You may want to re-populate the search index and clear your application cache after as well. See:
If it still doesn’t work, then you may want to check for data corruption. See:
Why do I get warnings when populating the search index?¶
If you’ve tried running the search:populate command (described in detail
here), and you see the following
warnings at the end of the console output:
Couldn't find information object (id: XXXXX)
Then Elasticsearch has encountered errors in your data, and was unable to find the listed information object IDs - consequently, these records have not been added to the search index, and will not be discoverable in the user interface via search and browse.
This warning suggests that there may be some corruption in your data. See the following section for further suggestions:
You can also get basic configuration and status information about your search index with the following command-line task:
Why do I get a SearchPhaseExecutionException when trying to search?¶
If you get an error like the following:
500 | Internal Server Error | Elastica\Exception\ResponseException
SearchPhaseExecutionException[Failed to execute phase [query_fetch], all shards failed]
This indicates an issue with Elasticsearch.
First, make sure that you have followed all the installation instructions for Elasticsearch, as outlined in our recommended installation documentation:
You can get basic configuration and status information about your search index with the following command-line task:
You can try restarting Elasticsearch with the following:
sudo systemctl restart elasticsearch
You can then try re-populating the search index and clearing the cache. See:
If this doesn’t resolve the issue and/or you are unable to run the
search:populate task, it may be that Elasticsearch is down. You can check
the status and health of your ES cluster with the following command: :
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health/?level=shards&pretty'
The status of shards must be green or yellow. If the status is any shard is red, you might want to try to restart Elasticsearch again.
The most common reason for ES failing to start is a lack of available system resources, such as not enough RAM, CPUs, and/or disk space. Elasticsearch also has its own configuration file - you might want to review the relevant ES set-up and configuration documentation:
- ES 1.7: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/1.7/setup-configuration.html
- ES 5.x: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.2/settings.html
For more information on troubleshooting Elasticsearch, see:
Why do I get a 504 Connection timed out error?¶
A 504 Gateway timeout error usually means that the server acting as a gateway to handle the HTTP request is either down or too slow to fulfill the request. This can occur for a number of reasons, and it could be temporary so the first thing you might want to try is simply repeating the request.
If the 504 timeout reoccurs, we suggest first restarting services, clearing the application cache, and then monitoring your resources while repeating the action that lead to the timeout. For information on restarting services and clearing the application cache, see:
Monitoring your system resources and active processes in real-time while repeating the action can also provide you with more information about where the bottleneck is occurring that is leading to the timeout. For information on monitoring, see above:
If you’re seeing spikes, then you may need to increase the available system resources (such memory, CPUs, and/or disk space).
You may also want to analyze your web logs - in many cases where we’ve seen
significant slowdowns in AtoM it’s due to search engine web crawlers making a
lot of requests in a short amount of time - often tens of thousands of
requests a day. We’ve had good results with adding a robots.txt
Crawl-delay
to slow down requests (30 is a good initial value to try) and blocking
particularly demanding or unwanted web crawlers. For more information, see:
- http://www.robotstxt.org/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robots_exclusion_standard
- https://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/robots-testing-tool
- https://varvy.com/robottxt.html
You can also look into increasing the execution limits configured for the site, so that more memory and time is made available before the limits are reached. More information can be found in the following sections:
Why am I seeing strange behavior in the AtoM treeview?¶
If you’re using the Sidebar treeview, double-check your Treeview settings (in Admin > Settings > Treeview) and ensure the sort is set to “Manual”. There are known issues with the other sort options, particularly if you have any descriptions missing an identifier or a title. For more context on this particular issue, see the following issue ticket:
If you’re using the Full-width treeview and you have recently used the drag-and-drop functionality to reorder sibling records in the treeview (described in the documentation here) and one of the moved records also has children, it’s possible that the background job to update the children has not yet completed. Wait a moment, and then refresh your browser. You can also check on the status of the job in the Jobs page - see:
If the job shows errors or refuses to complete, see the section above on Restarting the Job scheduler.
If none of the above is applicable, and/or you are still seeing issues, it could be that you need to rebuild the nested set. See:
You might want to clear all application caches after doing so, to ensure you are seeing the most up-to-date version of the page. See:
Don’t forget to clear your web browser’s cache as well!
If there are still issues and you’ve tried all of the above, then it is possible you are encountering some data corruption. See the following section:
Why can’t I upload (large) digital objects?¶
If you’re trying to upload digital objects via the user interface there are a couple things you can start to check. First, AtoM’s multi-file uploader (used to Upload multiple digital objects to archival descriptions at once) currently requires Flash to be installed and enabled in your web browser. If you can’t see any upload link, or you are constantly seeing an error in the widget when trying to upload an image, you may need to enable Flash.
Second, there have been reported issues with some browsers and the multi-uploader. Try using a different web browser and see if the outcome is different.
If the file is not huge but will not import via the user interface, you should
double-check the various settings available in AtoM that can be used to limit the
size and/or amount of digital objects. There is a global upload limit setting,
and a per-institution upload limit setting. In both cases, set the limit to
-1 for no limits on upload size. See:
- Default archival institution upload limit (GB)
- Set digital object upload limit for an archival institution
There is also a global upload limit maintained in one of AtoM’s
configuration files - specifically, the
config/app.yml file. You can also set this to -1 to disable upload limits.
See:
If the file never uploads, or the process times out while attempting the upload, then the file itself may be too large to import via the user interface. One important thing to note is that currently, the digital object uploads are performed synchronously - that is, on-demand, in real time, via the web browser. Because most web browsers have a built in timeout limit of about 1 minute (to prevent long-running requests from consuming all resources like memory and crashing your browser), your upload may fail if the digital object is too big.
Note that during installation, there is also a 64MB limit on
upload_max_filesize, which is maintained in your php.ini file. If you
continue to experience timeouts or are running into this size limitation, then
you may need to adjust your PHP execution limits. For more details, see:
There are 2 alternative methods of importing digital objects - either with
descriptive data in a CSV import, using the
digitalObjectPath or digitalObjectURI columns, or using the command-line
digitalobject:load task. These methods either make use of the job scheduler
to perform the import asynchronously in the background, or they are performed via
the terminal, avoiding the web browser and its timeout limits entirely. For more
information, see:
CSV import documentation
- CSV import (user interface)
- Import CSV files via the command-line
- Digital object-related import columns
Digital object load task
If you are receiving errors during upload, or the upload is happening but there are no local copies (like the thumbnail in search results) available, please make sure you have the following dependencies installed:
If you have them installed, you can try regenerating your digital object derivatives with the following command:
php symfony digitalobject:regen-derivatives
For more detailed documentation on this command-line task, see:
Why can’t I log into AtoM?¶
It could be that you’ve forgotten your correct password. If you need to reset it from the command-line, you can use the following task to change a user password:
Alternatively, you can temporarily create a new administrator account (AKA a “superuser”) via the command-line, so you can log in and update your previous password. You can then delete whichever account you no longer need from the command-line as well. See:
If the login button is not showing, it could be that it is simply hidden in
your theme. You can try navigating directly to the login page by adding
/user/login to your base URL. For example, if your AtoM site is normally
available at www.my-archives.com, try navigating to
www.my-archives.com/user/login.
If you are simply redirected to the homepage instead of seeing a login screen, then there are a few possibilities. The first is that you have turned on AtoM’s “Require SSL for all administrator functionality” setting in Admin > Settings > Security, but you do not currently have your SSL certificate properly configured for your AtoM site, or are trying to login via HTTP instead of HTTPS. For more on this setting, see: Security panel. Similarly, it could be that you (or someone else) has configured IP whitelist restrictions via the Security panel - ensure you are logging in from a white-listed IP.
If you have accidentally turned on the “Require SSL” setting and can’t log in, it’s possible to use SQL to disable this setting. For basic information on accesssing MySQL via the command-line, see: Accessing the MySQL command prompt. You will need to know the user and password you used for the database when installing AtoM, as well as the database name.
To use SQL to check and (if necessary) disable the SSL requirement setting, see:
The other reason you might be getting booted back to the home page whenever you
try to login is that it’s possible login for this installation is disabled via
a setting in one of AtoM’s configuration files
- specifically, the config/app.yml file.
Before you update this, double-check: is your installation using a 2-site deployment model (e.g. one internal read/write site, and a second public facing read-only catalog)? If yes, are you sure you are trying to log into the internal site, and not the public read-only site?
If you’ve checked that you’re trying to log into the correct site and you want
to ensure that the read_only setting is not engaged in your edit site, then
you will want to open the config/app.yml file via the command-line and
ensure that the read_only setting is set to false. See:
Important
There is also an environment variable maintained in /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php-fpm.conf
that can override the one in config/app.yml. We recommend checking both
files. In the atom.conf file, ensure that env[ATOM_READ_ONLY] is set
to “off” to disable this setting and allow users to log in again.
What should I do if I get an error that isn’t described here?¶
First, please go through the above sections of this document. Collect as much information as you can about the nature of the issue and how to reproduce it, as well as information on your particular installation environment. See:
Try restarting services, and/or some of the most common command-line tasks used for troubleshooting. See:
If these solutions don’t help, then you might want to search the AtoM user forum. Please review the following section of this document for tips on posting to the user forum:

